(a) Role of the diamond manufacturer
In the past, the roles of diamond cutting and polishing factories were simple. Procure the necessary rough diamonds, manufacture them, and distribute the finished diamonds at the wholesale level. Today, many manufacturers are purchasing the rough as close to the source (mines) as they can, and selling the finished diamonds as close to the retail level as possible. This has come about as a direct result of the manufacturer trying to raise the bottom line. Within the factories themselves, they have sought to create greater weight retention from the rough through modern technology.
Within the framework of diamond manufacturers worldwide, there is an organization that plays a major role on behalf of all diamond factories, The International Diamond Manufacturers Association (IDMA). This organization regulates standards and practices as well as look out for the welfare of all manufacturers as a whole.
The techniques employed in factories worldwide may be standard or specialized depending on the type of rough that is produced in each factory. The actual techniques used in processing a rough is very important to understand and will be dealt with in later assignments in this course.
We need to examine each of the major rough diamond manufacturing centers and look at how they affect the diamond market globally. The following chart will show the key role and position diamond manufacturers play in the diamond industry and ultimately the retail trade worldwide (Chart 1.2).
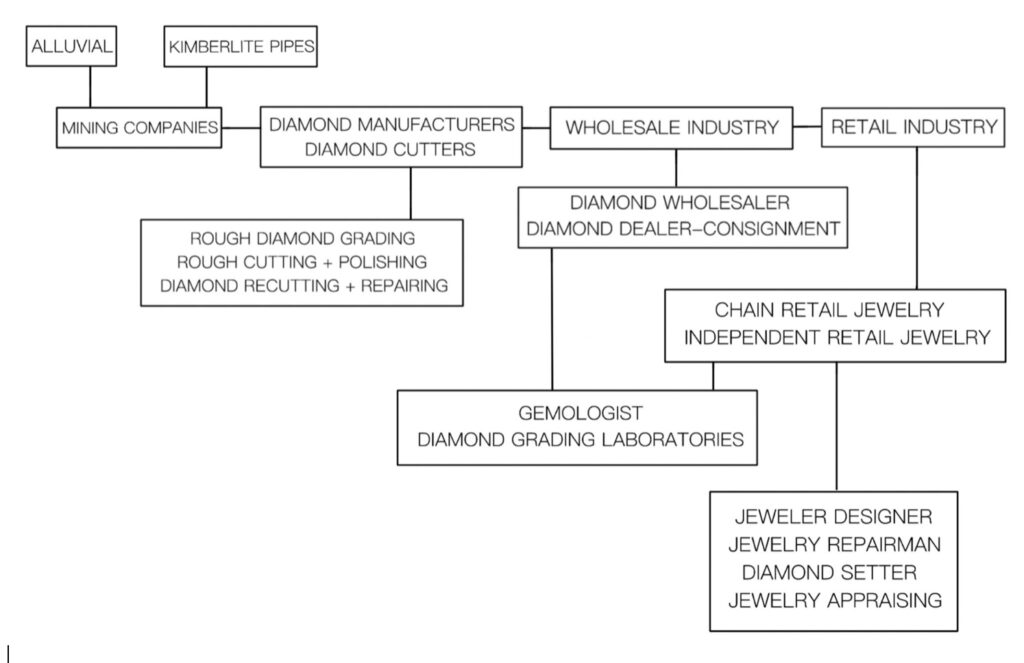
CHART 1 -2
(b) Belgium
The city of Antwerp, Belgium plays a significant role in both rough and finished diamonds. Antwerp has lost ground in recent years to Dubai and Mumbai, but approximately 80% of the world’s rough diamonds enter the Antwerp market at least ones. Much of this continues down the diamond pipeline to be cut and polished by manufacturers worldwide. The city of Antwerp hosts approximately one thousand branch offices, diamond factories, and trading companies. Antwerp has a yearly turnover in both polished and rough of approximately 54billion. Antwerp, Belgium will continue to play a major pivotal role in the diamond industry for the foreseeable future.
(c) Israel
Tel Aviv, Israel is considered another major player in the manufacturing and distribution of both rough and polished diamonds. In 2021 Israel’s total export of finished diamonds totaled 7.5 billion dollars, most of which was exported to the US.
Israel has opened, for the first time, a rough diamond bourse specifically designed to attract rough diamonds to the country of Israel. Israel’s manufacturers consider diamond technology vital to the success of its diamond industry. There is continued ongoing research and development in diamond technology. As a result, Israel is considered the leader in new diamond manufacturing equipment.
(d) India
India is no longer the stepchild in the diamond industry. Within the past twenty years, India has systematically placed itself squarely in the forefront of the industry. Today, India is responsible for over 80% of diamond cutting and polishing, in the world. It is the world-leading exporter in polished diamonds, in both volume and value. Total value of polished exports is over 22 billion dollars and expected to reach 30 billion USD by 2026.
On a yearly basis more than 100 million carats of both gem and near gem rough are manufactured in India. The Indian diamond industry employs directly and indirectly over one million production workers. To cope with the volume of rough that is manufactured on a yearly basis, India has steadily transformed its cutting and polishing factories with state-of-the-art equipment.
Many of the Indian manufacturers specialize in cutting and polishing the more difficult type of rough, a result from twinning and intergrowth. They have developed the skills and technological know-how to process both small and medium size rough.
In recent years there has been an excellent improvement in the quality of India’s polished diamonds. In future years, India will continue to be the leading manufacturer of rough diamonds.
(e) New York
New York is not a large diamond manufacturing center but is considered one of the most important because approximately 96% of U.S. diamond imports go through New York. The New York manufacturing industry contains approximately 80 diamond cutting companies. The diamond cutters are known for their high level of skill and ability to cut and polish medium to large sizes in rough. A large percentage of finished diamonds manufactured in New York are either ideal or close to ideal cut.
New York acts as the main distribution center to diamond wholesalers, diamond dealers and retail jewelers throughout the U.S. Diamond imports through New York exceed over six billion dollars. Rough diamond imports exceed eight million carats.
New York has the ability to quickly adapt and change according to retail demand. As a result, it is always ready to shift gears to meet market needs at the manufacturing level.